It is not unusual for customers to load very large data sets into their enterprise data warehouse. Whether you are doing an initial data ingestion with hundreds of TB of data or incrementally loading from your systems of record, performance of bulk inserts is key to quicker insights from the data. The most common architecture for batch data loads uses Google Cloud Storage(Object storage) as the staging area for all bulk loads. All the different file formats are converted into an optimized Columnar format called ‘Capacitor’ inside BigQuery.
This blog will focus on various file types and data loading tools for best performance. Data files that are uploaded to BigQuery, typically come in Comma Separated Values(CSV), Avro, Parquet, JSON, ORC formats. We are going to use a large dataset to compare and contrast each of these file formats. We will explore loading efficiencies of compressed vs. uncompressed data for each of these file formats. Data can be loaded into BigQuery using multiple tools in the GCP ecosystem. You can use the Google Cloud console, bq load command, using the BigQuery API or using the client libraries. We will also compare and contrast each loading mechanism for the same dataset. This blog attempts to elucidate the various options for bulk data loading into BigQuery and also provides data on the performance for each file-type and loading mechanism.
Introduction
There are various factors you need to consider when loading data into BigQuery.
-
Data file format
-
Data compression
-
Tool used to load data
-
Level of parallelization of data load
-
Schema autodetect ‘ON’ or ‘OFF’
Data file format
Bulk insert into BigQuery is the fastest way to insert data for speed and cost efficiency. Streaming inserts are however more efficient when you need to report on the data immediately. Today data files come in many different file types including comma separated(CSV), json, parquet, avro to name a few. We are often asked how the file format matters and whether there are any advantages in choosing one file format over the other.
CSV files (comma-separated values) contain tabular data with a header row naming the columns. When loading data one can parse the header for column names. When loading from csv files one can use the header row for schema autodetect to pick up the columns. With schema autodetect set to off, one can skip the header row and create a schema manually, using the column names in the header. CSV files can use other field separator/newline characters too as a separator, since many data outputs already have a comma in the data. You cannot store nested or repeated data in CSV file format.
JSON (JavaScript object notation) data is stored as a key-value pair in a semi structured format. JSON is preferred as a file type because it can store data in a hierarchical format. The schemaless nature of json data rows gives the flexibility to evolve the schema and thus change the payload. JSON and XML formats are user-readable, but JSON documents are typically much smaller than XML. REST-based web services use json over other file types.
Parquet is a column-oriented data file format designed for efficient storage and retrieval of data. Parquet compression and encoding is very efficient and provides improved performance to handle complex data in bulk.
Avro: The data is stored in a binary format and the schema is stored in JSON format. This helps in minimizing the file size and maximizes efficiency. Avro has reliable support for schema evolution by managing added, missing, and changed fields.
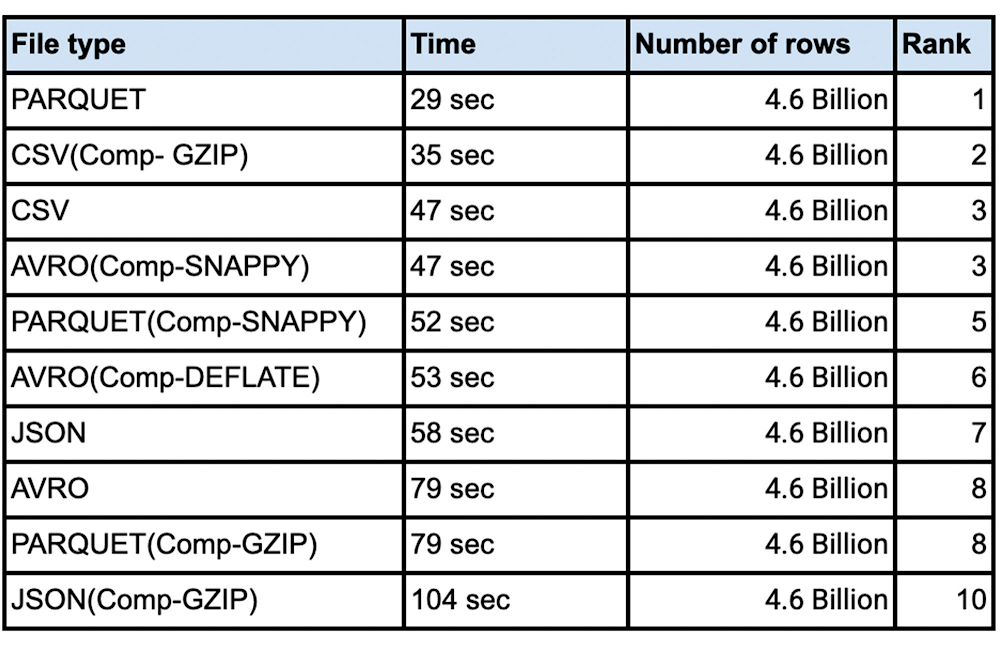
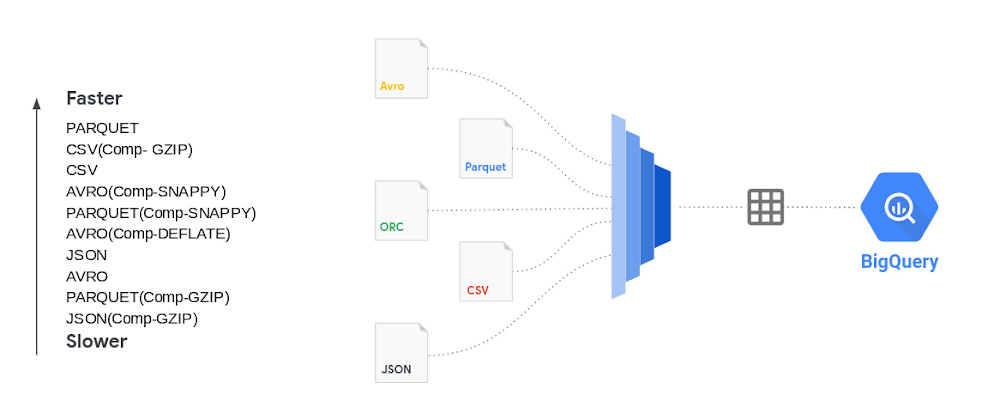
From a data loading perspective we did various tests with millions to hundreds of billions of rows with narrow to wide column data .We have done this test with a public dataset named `bigquery-public-data:worldpop.population_grid_1km`. We used 4000 flex slots for the test and the number of loading slots is limited to the number of slots you have allocated for your environment, though the load slots do not use all of the slots you throw at it.. Schema Autodetection was set to ‘NO’. For the parallelization of the data files each file should typically be less than 256MB for faster throughput and here is a summary of our findings:

Do I compress the data?
Sometimes batch files are compressed for faster network transfers to the cloud. Especially for large data files that are being transferred, it is faster to compress the data before sending over the cloud Interconnect or VPN connection. In such cases is it better to uncompress the data before loading into BigQuery? Here are the tests we did for various file types with different compression algorithms.Shown results are the average of five runs:
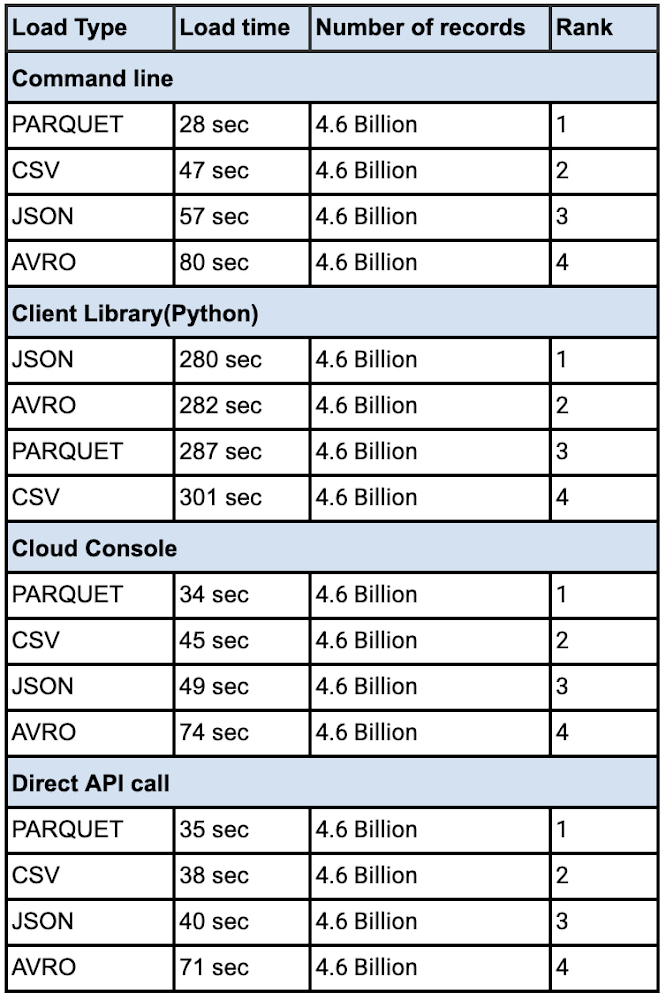
How do I load the data?
There are various ways to load the data into BigQuery. You can use the Google Cloud Console, command line, Client Library(shown python here) or use the Direct API call. We compared these data loading techniques and compared the efficacy of each method. Here is a comparison of the timings for each method. You can also see that Schema Autodetect works very well, where there are no datatype quality issues in the source data and you are consistently getting the same columns from a data source
Conclusion
There is no advantage in loading time when the source file is in compressed format. In fact for the most part uncompressed data loads in the same or faster time than compressed data. We noticed that for csv and avro file types you do not need to uncompress for faster load times. For other file types including parquet and json it takes longer to load the data when the file is compressed. Decompression is a CPU bound activity and your mileage varies based on the amount of load slots assigned to your load job. Data loading slots are different from the data querying slots. For compressed files, you should parallelize the load operation, so as to make sure that data loads are efficient. Split the data files to 256MB or less to avoid spilling over the uncompression task to disk.
From a performance perspective avro, csv and parquet files have similar load times. Use the command line to load larger volumes of data for the most efficient data loading. Fixing your schema does load the data faster than schema autodetect set to ‘ON’. Regarding ETL jobs, it is faster and simpler to do your transformation inside BigQuery using SQL, but if you have complex transformation needs that cannot be done with SQL, use Dataflow for unified batch and streaming, Dataproc for open source based pipelines, or Cloud Data Fusion for no-code / low-code transformation needs.
To learn more about how Google BigQuery can help your enterprise, try out Quickstarts page here.
Disclaimer: These tests were done with limited resources for BigQuery in a test environment during different times of the day with noisy neighbors, so the actual timings and the number of rows might not be reflective of your test results. The numbers provided here are for comparison sake only, so that you can choose the right file types, compression and loading technique for your workload.